Poland in the ranking of the Responsible Development Index

Poland in the ranking of the Responsible Development Index
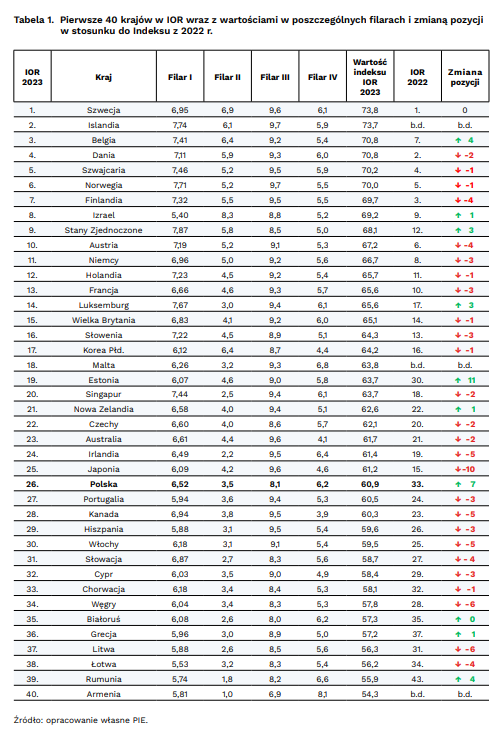
Poland has risen from 33rd place in 2021 to 26th in 2022 in the Responsible Development Index compiled by the Polish Economic Institute since 2019. This is the only progress among the Visegrad Group countries. The Nordic countries once again dominate the top half of the rankings, taking up half the places in the top ten.
Poland has risen from 33rd place in 2021 to 26th in 2022 in the Responsible Development Index compiled by the Polish Economic Institute since 2019. This is the only progress among the Visegrad Group countries. The Nordic countries once again dominate the top half of the rankings, taking up half the places in the top ten.
The Index for Responsible Development (IOR) was created as an alternative to GDP and allows a more accurate representation of changes taking place in individual countries.
The IOR has 4 components: current prosperity, creating future prosperity, non-wage factors, climate responsibility. The index is compiled based on 9 indicators. Data are taken, inter alia, from databases of the World Bank, the European Commission or the United Nations. The latest analysis looked at 40 countries.
Nordic countries top the rankings
Nordic countries consistently dominate among the countries with the highest IOR values. This is due to the harmonious combination of economic, social and environmental aspects in the development strategies of these countries. Sweden took first place overall, despite not winning in individual categories. This indicates a balance between individual aspects of development. Scandinavian countries achieve the highest scores in non-financial categories such as life expectancy. They live the longest in Norway, Sweden, Iceland and Denmark. High results are also associated with safety, a clean environment and the health of citizens.
Among the 40 countries with the highest index scores, more than 75 percent are European countries. This is mainly due to the good performance in the areas of education expenditure and research and development (pillar II) as a percentage of GDP. In Western Europe, the indicator fluctuated in the range of 4.5-6 points, and throughout the European Union it was, on average, 3.9 points. Outside Europe, these values were lower, for example, in Singapore they were 2.5 points, in Canada - 3.8 points. It is worth noting that lower values of this component are also observed in Europe, in countries known as tax havens, for example, Luxembourg (3.0), Malta (3.2) and Ireland (2.2).
Inflation is the main challenge to prosperity
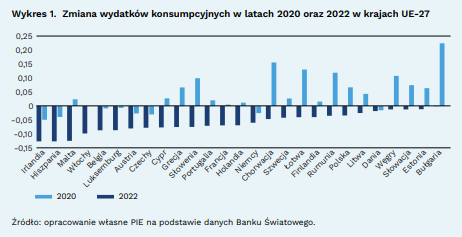
In October 2022, inflation in the eurozone reached a record high of 10.6%. This was mainly a result of the supply chain crisis and the conflict between Russia and Ukraine. Food and energy prices have also increased significantly. Rising inflation weakened household consumer spending. The amount of expenditure per household in nominal terms decreased by 4.3% (from 9.2 to 8.8 thousand US dollars).
Consumption in the European Union is still higher than before the pandemic (on average by about 3.3%), despite the decline in real wages. The highest growth in consumer spending is observed in Bulgaria (22% compared to 2020), Croatia (15%) and Latvia (13%). In Poland, consumption growth in 2020-2022 was 6.7%.
The year 2022 brought a marked shift in global development with an exceptional emphasis on economic stability and social well-being. The Nordic countries continue to develop steadily. Due to the unprecedented rise in energy prices caused by problems in global markets caused by the COVID-19 pandemic and events in Ukraine (for example, the price of gas increased from 69 PLN/MWh in 2020 to 600 PLN/MWh in 2022), many European countries decided to introduce protective mechanisms so as not to pass on all the costs of the energy crisis to consumers. Action took various forms - for example, the Spanish government abolished the 7% tax on energy production, and the Polish government decided to impose restrictions on the prices of thermal energy and water.
Promotion of Poland in the IOR ranking as the only country from the Visegrad Group
Poland rose in the ranking of the Responsible Development Index from 33rd to 26th place, the only country in the Visegrad Group. This is mainly the result of an increase in net income and consumption in 2022. Consumer spending grew more strongly than in EU countries. Other countries saw declines: the Czech Republic dropped from 20th to 22nd place, Hungary from 28th to 34th and Slovakia from 27th to 31st.
There are still areas for improvement in Poland. In the category of non-wage factors (pillar III), the average result of both the Visegrad Group and Poland was below the European Union average and decreased compared to the previous study. The reason for the regression was the COVID-19 pandemic and excessive mortality, which led to a reduction in life expectancy. In component II - expenditure on R&D and education as a percentage of GDP, on average for the Visegrad Group is also lower than for the EU - 3.6% versus 3.9%.
On the other hand, the Visegrad Group achieved the best result in pillar IV – Climate Responsibility (5.7 versus 5.6% in the EU), while Poland had the highest score in this pillar in the group (6.2%). This is the result of a significant reduction in CO2 emissions compared to the base year 1990.
Source: pie.net.pl
Blog

Current trends in housing construction in Poland
Current trends in housing construction in Poland


Average prices for secondary housing in Warsaw districts in December 2023
Average prices for secondary housing in Warsaw districts in December 2023





